|
| Diver using
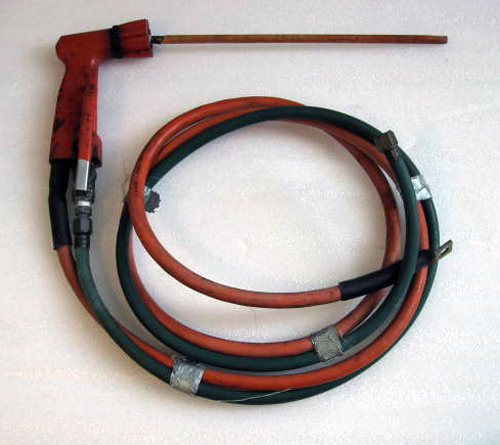
Oxy-hydrogen underwater cutting equipment. |
Oxy-electric was first used in the early 20th century. Electrodes are used which are made of steel or carbon. The surface to be cut is heated to the point of melting which is done by the electric arc. The electrode is tubular and oxygen passes through the bore of the rod or electrode. As soon as the electric arc is formed or 'struck' intense heat begins to melt the metal . A trigger is depressed and a stream of oxygen oxidises the molten metal . The electric current required is 550 amps with a DC voltage of 70-90 volts. Oxy-arc cutting is more suitable for cutting thinner metal as well as cast iron or non -ferrous metals. Coloured glasses are required for the oxy-electric process as the arc is intensely bright and damage to the eyes can easily occur giving rise to the condition known as Arc-eye.